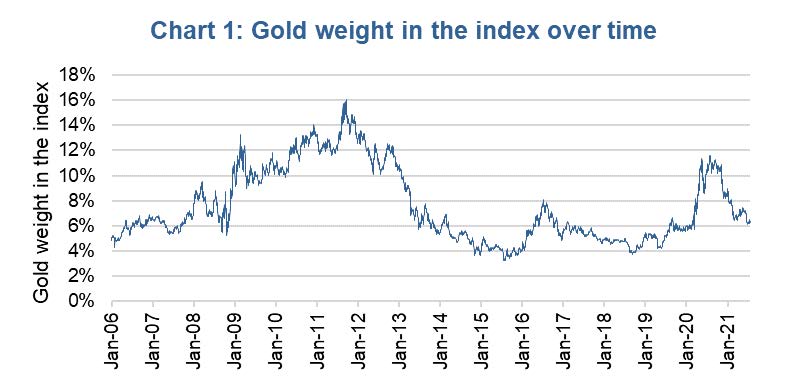
The reason we decided to discuss gold in this week’s edition is that we are seeing some odd pricing behaviour in the yellow metal of late. The price of gold is often heavily influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Inflation – since gold is a real asset, it is often viewed as a hedge against inflation. Higher inflation, higher gold.
- Nominal yields – given gold has no distribution, higher nominal yields on government bonds makes that competing defensive asset class relatively more attractive. High yields, lower gold.
- U.S. dollar hedge – Gold is quoted in USD, so a falling USD is typically positive for gold prices. Lower USD, higher gold.
- Trust – gold often does well as a hedge against uncertainty, including trust in the financial system. Lower trust, higher gold.
There are other factors as well. Bitcoin has become a competing asset class to some degree for those desiring a non-fiat currency alternative. Central bank buying or selling gold, flows into gold ETFs, consumer demand especially from developing economies … the list goes on. But the four we listed are usually big and more consistent factors.
To make matters a bit more complex, the influence of these factors changes over time. For instance, sometimes gold reacts to inflation but ignores currency or nominal yield moves. Sometimes currency moves matter the most for gold, and other factors don’t matter. Nobody ever said investing would be easy.
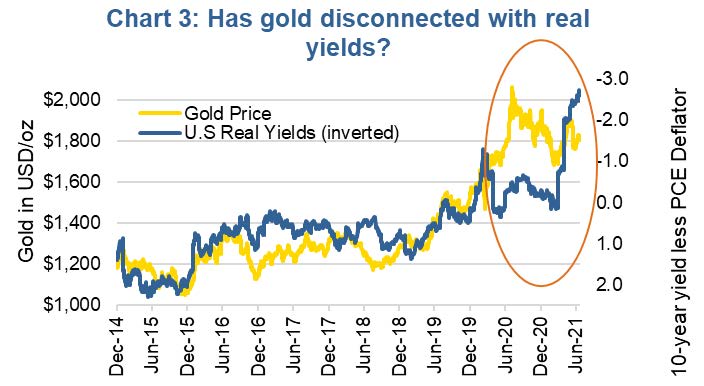
Gold misbehaving
Real yields, which is the nominal 10-year U.S. Treasury yield less inflation, captures both nominal yields and inflation factors listed above. There has been a very strong connection between gold bullion prices and real yields for the past decade. In addition, peaks and troughs in real yields have often coincided with troughs and peaks in gold prices going back to the 1970s (Chart 2). Turning points in the direction of real yields has marked turning points in gold. Plus, when real yields are trending in one direction, gold is often trending in the opposite [note: real yields are inverted in the charts].
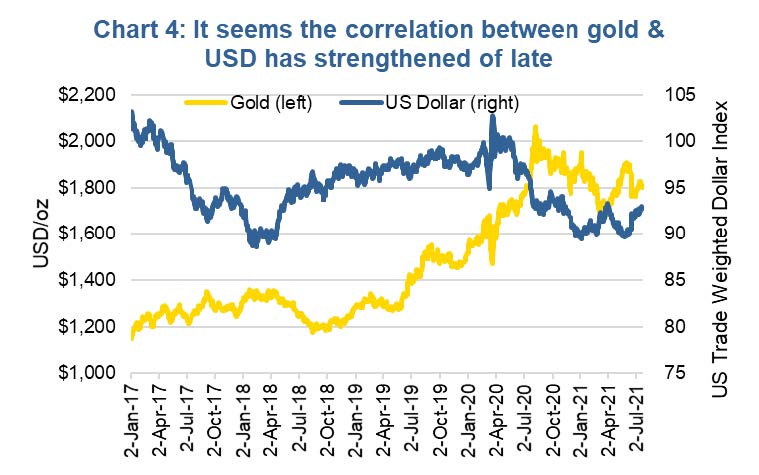
For the other factors we are not sure how to measure ‘trust’ in the system, but we will point out that currency appears to be having a stronger influence on gold in the past few months. Normally, when the U.S. dollar declines, gold rises and vice versa. This relationship has been very soft or even moving against the norm since 2019 and into early 2021, for the most part. Gold started rising in 2019 despite a rising USD. In late 2020, gold continued to rise as the USD started to weaken (normal), but the USD continued to weaken and gold reversed course. The past few months though, we have seen them moving in opposite directions again (Chart 4).
Charts are sourced to Bloomberg L.P. unless otherwise noted.
The contents of this publication were researched, written and produced by Richardson Wealth Limited and are used herein under a non-exclusive license by Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”) for information purposes only. The statements and statistics contained herein are based on material believed to be reliable but there is no guarantee they are accurate or complete. Particular investments or trading strategies should be evaluated relative to each individual's objectives in consultation with their Echelon representative.
Forward Looking Statements
Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections based on beliefs and assumptions made by author. These statements involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
The opinions expressed in this report are the opinions of the author and readers should not assume they reflect the opinions or recommendations of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. or its affiliates. Assumptions, opinions and estimates constitute the author’s judgment as of the date of this material and are subject to change without notice. We do not warrant the completeness or accuracy of this material, and it should not be relied upon as such. Before acting on any recommendation, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, if necessary, seek professional advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. These estimates and expectations involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
The particulars contained herein were obtained from sources which we believe are reliable, but are not guaranteed by us and may be incomplete. The information contained has not been approved by and are not those of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”), its subsidiaries, affiliates, or divisions including but not limited to Chevron Wealth Preservation Inc. This is not an official publication or research report of Echelon, the author is not an Echelon research analyst and this is not to be used as a solicitation in a jurisdiction where this Echelon representative is not registered.
The opinions expressed in this report are the opinions of its author, Richardson Wealth Limited (“Richardson”), used under a non-exclusive license and readers should not assume they reflect the opinions or recommendations of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”) or its affiliates.
This is not an official publication or research report of Echelon, the author is not an Echelon research analyst and this is not to be used as a solicitation in a jurisdiction where this Echelon representative is not registered. The information contained has not been approved by and are not those of Echelon, its subsidiaries, affiliates, or divisions including but not limited to Chevron Wealth Preservation Inc. The particulars contained herein were obtained from sources which we believe are reliable, but are not guaranteed by us and may be incomplete.
Assumptions, opinions and estimates constitute the author’s judgment as of the date of this material and are subject to change without notice. Echelon and Richardson do not warrant the completeness or accuracy of this material, and it should not be relied upon as such. Before acting on any recommendation, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, if necessary, seek professional advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. These estimates and expectations involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections based on beliefs and assumptions made by author. These statements involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.