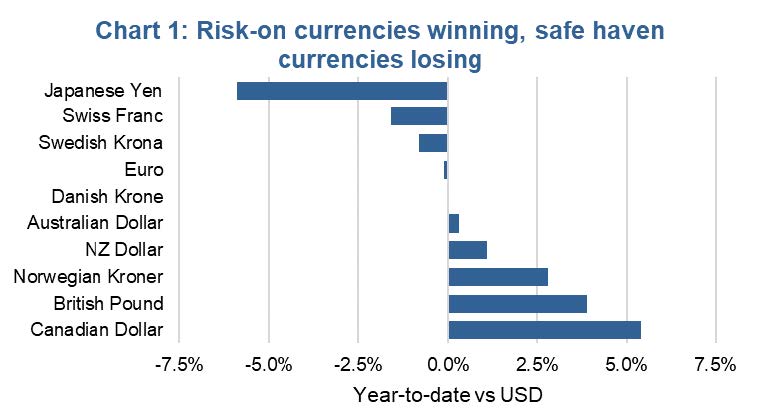
Versus the USD it is clear 2021 has seen risk-on currencies such as the CAD, Norwegian kroner and Australian dollar performing much better. Meanwhile safe haven currencies including the yen and Swiss Franc have been laggards. The USD is also considered a safe haven currency. With global growth accelerating out of the pandemic, this has been a risk-on currency friendly market.
CAD Tailwinds
There are many contributing factors that have helped the CAD rise to 83 cents. Everyone would agree the Bank of Canada and the U.S. Federal Reserve remain dovish by any historical metric, including the overnight lending rates and active bond buying activities (quantitative easing). However, it is the relative moves or the degree of dovishness that has favoured the CAD. The Bank of Canada has started to reduce its quantitative easing while the Fed continues. One would be hard pressed to call the Bank of Canada hawkish, but in this crazy money printing world, less dovish is the new hawkish.
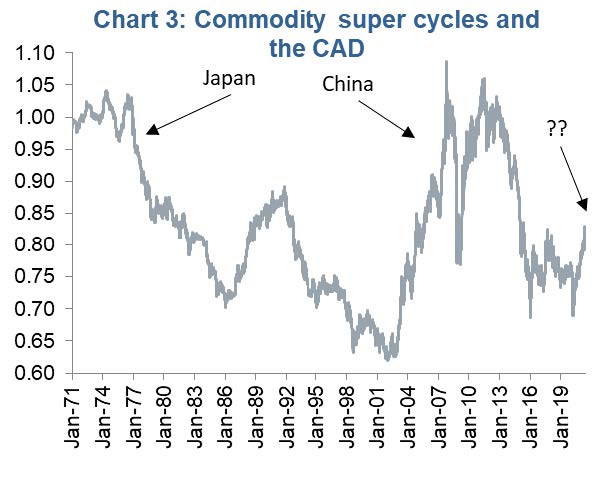
Perhaps the biggest tailwind of late for the CAD has been the rise in commodity prices. Like it or not, our currency is viewed in the global currency markets as a commodity currency. And the rise in commodity prices has many posturing or wondering if we are in the early innings of a new commodity super cycle. (chart 2).
If you believe we are in a commodity super cycle, the CAD has further upside potential. This is not our investment committee’s view. While many commodity prices have appreciated to levels not seen since the last commodity super cycle, we believe this is a temporary phenomenon for a few reasons. The most obvious is changed consumer behaviour during the social distancing of the pandemic has resulted in increased spending on durable goods. Durable goods require more commodities than non-durables and services. This behaviour change has caused a demand spike for commodities while logistics and capacity remain constrained due to the pandemic. We believe this demand spike will fade with re-opening and supply chain bottlenecks ease.
To have a new commodity super cycle, the world requires consistently high aggregate demand growth over many years. Similar to the ones experienced during the rapid industrialization of Japan or urbanization of China (chart 3). We do not see one of these secular demand shifts developing and believe this commodity price spike will fade. Along with it, so will the strength in the Canadian dollar.
Where to from here?
There are many reasons to be both bullish the CAD and bearish the CAD, in USD terms. In the short-term the CAD bulls can cite global growth recovery, the magnitude of stimulus in the U.S. economy, commodity prices and relative yields being pretty tight. Longer term, well there are often rumblings of the U.S. gradually losing its reserve currency status as global trade becomes more balanced.
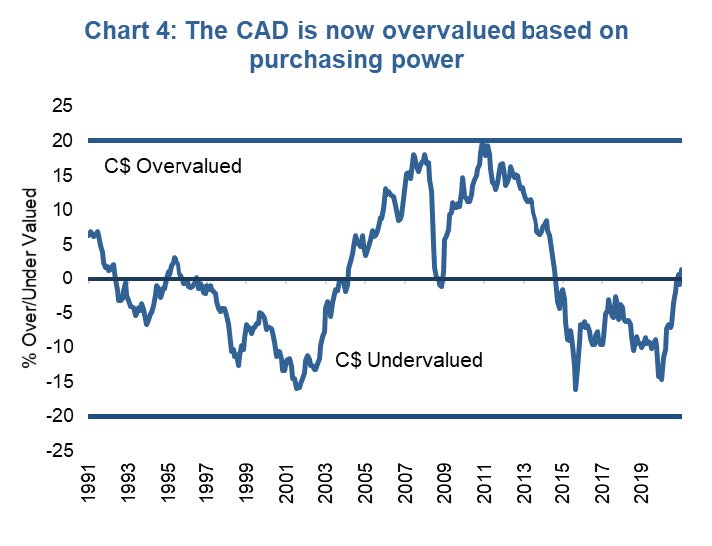
In the short-term CAD bears can cite the CAD is already ‘expensive’ at 83 cents (chart 4). Plus, many of the above-mentioned reasons to be bullish on the CAD are short-term and likely to normalize. Once that border opens, there will be a flood of citizens wanting to spend our CAD outside the country. This flood is likely bigger than the inbound tourists. The US economy is doing much better than Canada, which will translate into yields over time. And longer term, as yields rise given Canada’s relative indebtedness, this tempers our economic outlook even further.
Charts are sourced to Bloomberg L.P. unless otherwise noted.
The contents of this publication were researched, written and produced by Richardson Wealth Limited and are used herein under a non-exclusive license by Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”) for information purposes only. The statements and statistics contained herein are based on material believed to be reliable but there is no guarantee they are accurate or complete. Particular investments or trading strategies should be evaluated relative to each individual's objectives in consultation with their Echelon representative.
Forward Looking Statements
Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections based on beliefs and assumptions made by author. These statements involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
The opinions expressed in this report are the opinions of the author and readers should not assume they reflect the opinions or recommendations of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. or its affiliates. Assumptions, opinions and estimates constitute the author’s judgment as of the date of this material and are subject to change without notice. We do not warrant the completeness or accuracy of this material, and it should not be relied upon as such. Before acting on any recommendation, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, if necessary, seek professional advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. These estimates and expectations involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
The particulars contained herein were obtained from sources which we believe are reliable, but are not guaranteed by us and may be incomplete. The information contained has not been approved by and are not those of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”), its subsidiaries, affiliates, or divisions including but not limited to Chevron Wealth Preservation Inc. This is not an official publication or research report of Echelon, the author is not an Echelon research analyst and this is not to be used as a solicitation in a jurisdiction where this Echelon representative is not registered.
The opinions expressed in this report are the opinions of its author, Richardson Wealth Limited (“Richardson”), used under a non-exclusive license and readers should not assume they reflect the opinions or recommendations of Echelon Wealth Partners Inc. (“Echelon”) or its affiliates.
This is not an official publication or research report of Echelon, the author is not an Echelon research analyst and this is not to be used as a solicitation in a jurisdiction where this Echelon representative is not registered. The information contained has not been approved by and are not those of Echelon, its subsidiaries, affiliates, or divisions including but not limited to Chevron Wealth Preservation Inc. The particulars contained herein were obtained from sources which we believe are reliable, but are not guaranteed by us and may be incomplete.
Assumptions, opinions and estimates constitute the author’s judgment as of the date of this material and are subject to change without notice. Echelon and Richardson do not warrant the completeness or accuracy of this material, and it should not be relied upon as such. Before acting on any recommendation, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, if necessary, seek professional advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. These estimates and expectations involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections based on beliefs and assumptions made by author. These statements involve risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance or results and no assurance can be given that these estimates and expectations will prove to have been correct, and actual outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed, implied or projected in such forward-looking statements.